Wealth creation (from waste) In an
organization
from the Engineering Industry
- The organization had a high internal rejection of Rs 30 lakhs for the year ended 2015 against an annual turnover of Rs 25+ cr.
- They were able to meet only less than 80% of their monthly production schedule.
- There was an absence of daily management and measurement systems and hence they were unable to monitor Productivity, Quality and Cost.
- All this led to losses for the last 3 years in a row, high rejections and not able to meet delivery commitments consistently.
- OEE Data gathering and setting up systems to capture data
- Formation of Cross Functional Team
- Prioritising key contributors to business loss
- High changeover or setting time
- Issues with Die that lead to quality problems and adjustments
- High Machine down time
- Application of tools and techniques
- Periodic Review
The Case studies describes the methodology of creating wealth from waste through the „Essae Wealth from Waste‟ cluster in an organization from the engineering industry. The cluster was structured to ensure progress was reviewed by the Cluster Anchor every 15 days. Tools & Techniques were explained in a classroom session, along with other cluster members. The team had 15 days to implement the Learnings on the shop floor. This was reviewed by the anchor during a plant visit and inputs were given. The team took corrective action and presented progress to the anchor & other cluster members, after the next 15 days. Inputs were taken from other cluster members as well. This cycle was continued for 12 months.
A. Background
An organisation from the engineering industry, established in 2006 approached the Essae Chandran Institute with a need to improve their production process. They were making losses for the last 3 years.
The organization caters to requirements of automobile and engineering industries. The facilities are appropriate to cater to the requirements of customers with complex design and manufacturing processes. The company has a production facility with total capacity of 1000 – 2500 Tonnes. In addition to the production shop, its infrastructure also consists of quality assurance lab, tool room facility, heat treatment facility, CNC milling centres. It is an ISO:9001:2008 certified company
B. Business challenges faced
C. Approach to the challenges
The first step was to set up systems to gather data and assess losses or waste in the operations so that constraints within the production process could be identified. It was done through educating the team and implementing organisation wide performance metrics (KPI’s). Targets were fixed for one year and OEE measurement in operations was introduced.
A cross functional team was formed involving the Managing Director, the production head and the shop floor personnel in charge of the respective processes. The team was made accountable for the achievement of the KPI and OEE targets within a specific time frame.
After monitoring and analysing OEE data, the cross functional team, prioritised top 3 issues that were the major contributors to production cost over-run and delivery delays. They were:
To eliminate or reduce the identified wastes , the following lean tools were used - Structured Problem Solving Techniques, 5S, Visual Management, Root Cause Analysis, Zero Defect techniques, Continuous improvements, SMED, Flow Mgmt / Line Balancing.
For example, to reduce changeover time, the team was taught SMED to analyze internal and external elements in a structured manner. By applying simplification and reengineering principles they were able to reduce internal elemental time and by practicing housekeeping and visual management techniques, they were able to improve external elemental time. The entire exercise was facilitated the by the Anchor.
The core team met on a weekly basis to track progress and discuss solutions. The challenge was to get the team oriented to observation and data collection, identifying the constraints and monitoring OEE measurement. The benefit of data gathering & monitoring was highlighted to the organisation and its employees. It improved communication among the team and brought about an increase in employee engagement levels. This brought about a slight positive cultural shift in the organisation.
Progress was reviewed on a bimonthly basis with inputs from the anchor.
D. Benefits observed
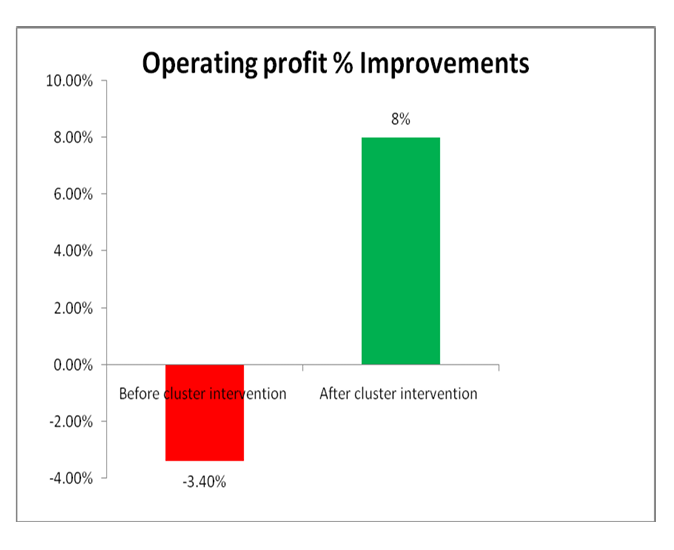
At the end of the cluster, the
organization recorded Positive
Operating profit of 8 % a
massive increase from the
losses incurred of the last 3 years.
This was a result of:
- 1. Increase in Sales Turnover by 20 % with the
existing customer base
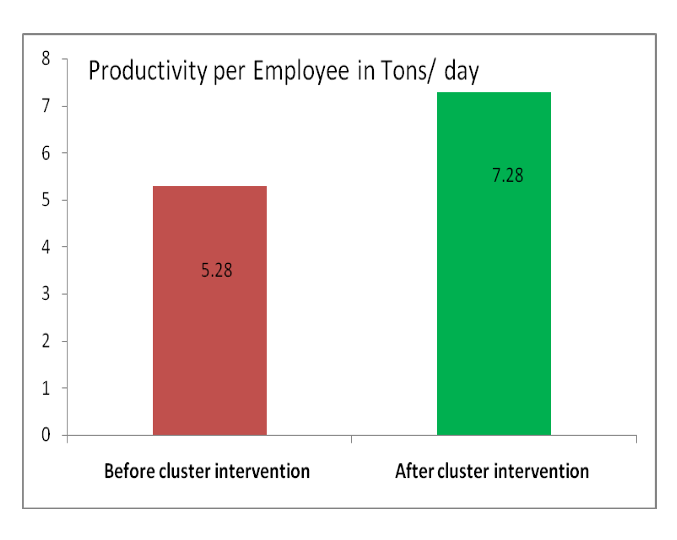
2. Increase in Productivity per employee from 5.28 tons to 7.28 tons per day
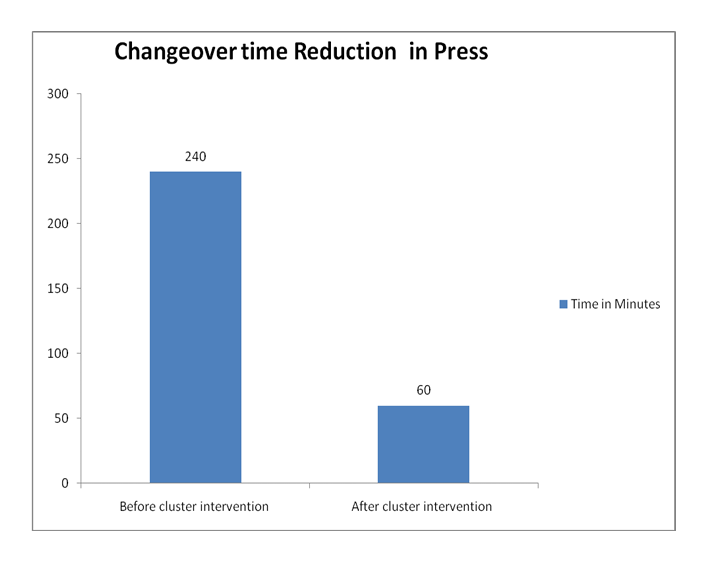
3. Reduction in Changeover time from 240 min to 60 min
4. Increase in Die tool life and reduction in Die cost by 90 %
5. Increase in material yield by 8 %
6. Plant capability to deliver was improved to 100 % from less than 80 % due to OEE improvements
7. Variation correction time reduced from 60 minutes to 4 minutes
E. Conclusions Recommendations for growth & sustainability
The scope for productivity improvement is vast in the engineering industry. The key is
establishing
measurement systems monitoring them for OEE improvement. Periodic reviews of OEE and KPI
is crucial for growth
and sustainability, especially in an environment of increased competition and increased
costs.
The organization must sustain the practice of 5S, House Keeping, Visual Management &
Root
Cause Analysis and Zero Defect technique.
An expansion of customer base is crucial for increase in the sales revenue.
There is further scope for reduction in set up time from 60 minutes to 20 minutes and
the team is advised to continue in this pursuit.
The anchor has also advised a keen focus on maintenance activity to further reduce
machine down time and optimize material handling by
having material accountability from order till dispatch
The organization, to stimulate growth has to relook at their organization structure and
look to
fill key positions. It is also recommended to initiate employee engagement initiatives
to sustain the improvements and take the
organization to next level growth anprofitability.
The organization caters to requirements of automobile and engineering industries. The facilities are appropriate to cater to the requirements of customers with complex design and manufacturing processes. The company has a production facility with total capacity of 1000 – 2500 Tonnes. In addition to the production shop, its infrastructure also consists of quality assurance lab, tool room facility, heat treatment facility, CNC milling centres. It is an ISO:9001:2008 certified company
